STOOL HEALTH REMEDIES
|
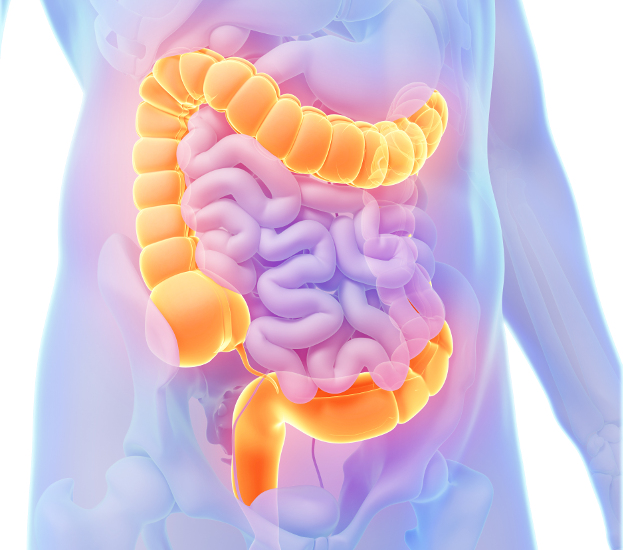
The stool is called Mala in Ayurveda.  Categories in PoopStoolStool ColorElimination / Bowel RoutineOverviewDon't know your body type? Take our free Dosha quiz!
TAKE THE QUIZ
29 likes This type of stool indicates a healthy, well-formed stool. The ideal poop is like a banana in size, shape and consistency with a medium brown color and no cracks on the surface. The bowels should eliminate 1-2x daily, with the first movement in the... 19 likes Cracks on the surface of a stool indicate moderate dryness of the stool and dehydration. The stool may be sitting in the bowels for too long. As the stool sits in the bowels, the intestines continue to absorb water from them, making the stool into a...      (4.00 out of 5 stars) 1 rating, 46 likes (4.00 out of 5 stars) 1 rating, 46 likesA smooth surface on stool indicates the stool is well hydrated. A long stool indicates adequate fiber or poor absorption. The ideal poop is like a banana in size, shape and consistency with a medium brown color and no cracks on the surface. The bowels... 12 likes The satisfying daily release of a long, large lincoln log stool indicates adequate soluble and insoluble fiber in the diet. The fiber absorbs moisture which increases the size of the stool. Constipation accompanied by a long, large stool can... 163 likes Small, hard stool indicates either dryness in the colon or that the stool is sitting in the colon for too long. Hard, dry stools are considered to be a sign of constipation. When stool sits in the colon too long, it begins to rot. The rotting stool... 27 likes Have you ever seen air bubbles in your poop? Is your poop frothy? Frothy poop is a sign of poor digestion. When food digests poorly, it sits too long in your gut and bacteria begin to grow. This causes fermentation, the same process that... 17 likes Irritation, inflammation and osmotic laxatives can often cause stools to completely liquefy. This condition quickly depletes the body of fluids and electrolytes, causing weight loss and dehydration. The loss of electrolytes can lead to muscle cramps... 32 likes Stool in pieces mixed with liquid should be differentiated from mud-like stool. Mud like stool is stool that has never formed into a solid. Mushy pieces imply the stool was formed, then mixed with liquids, perhaps implicating the colon. When the lining... 16 likes About Foamy Poop Frothy stools are those that contain bubbles and look somewhat like a foamy poop. Frothy stools mean there is a lot of air mixed with the stool due to gut fermentation. The bubbles in foamy stool are produced by... 34 likes Stool that is thick mud can imply that digestive organs are too weak to fully digest the food (Vata). Or, muddy stools can reflect a diet that is too rich. It may also be a sign of excess bile (Pitta). If the stool has a foul odor, it is a hot & sour... 186 likes When stools are soft, you lose vital fluids and electrolytes. When stools are soft, there is often poor absorption of foods. You may feel drained & tired. The longer your stools are soft, the more your ojas will be depleted. Stools become soft for... 23 likes Narrow Stools (Stringy poop, Pencil stool) can indicate inflammation or growths in the colon causing a stricture (narrowing of the inside of the tube). The inflammation can obstruct the movement of stools. It can also be a simple sign of loose stools... 8 likes A polyp, internal hemorrhoid, or something protruding into the colon can create a consistent groove in the stool. This condition should be checked by a qualified gastroenterologist to rule out colon cancer. 15 likes Passing a parasite in your stool is a definitive sign you have parasites. Parasites are organisms that live within another organism, often causing harm to the host. They can live in multiple locations in the human body, but many prefer the digestive... 28 likes Skins of foods, poorly chewed foods, and foods that are difficult can be seen in the stools. Undigested food is often a sign of a low digestive fire. Poor digestion may be due to a blood deficiency, stress, poor routine & eating habits, or eating... 53 likes The body doesn't make foul odors. Odorous stool implies food is rotting and fermenting in the gut. Poop starts to rot when it sits too long in the gut (constipation). When you cannot absorb the nutrients from your food (malabsorption, Vata), the... 
AYURVEDIC FACE ASSESSMENT
Learn how to assess constitution by a person's face.
|
Join Joyful Belly.
Want our top Ayurvedic recipes and health tips?Subscribe to our free newsletter!








 SAVE SYMPTOM
SAVE SYMPTOM